Cerebellar Lesions and Nystagmus: Unraveling the Connection
As a neuro-ophthalmologist specializing in nystagmus, I’ve seen firsthand how cerebellar lesions can significantly impact eye movements. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the fascinating relationship between cerebellar damage and nystagmus, exploring its causes, types, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Why Does Nystagmus Occur in Cerebellar Lesions?
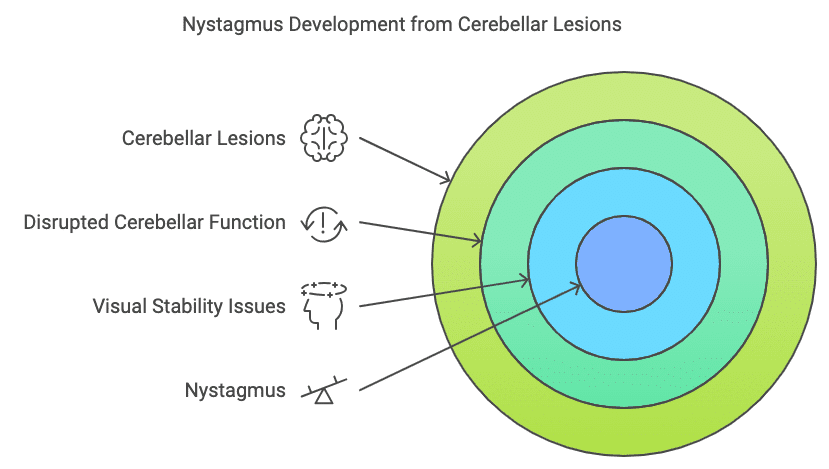
Nystagmus, the involuntary rhythmic oscillation of the eyes, often serves as a telltale sign of cerebellar dysfunction. But why does damage to this part of the brain cause such distinctive eye movements?

The cerebellum plays a crucial role in maintaining balance, coordinating movements, and fine-tuning motor control. When it comes to eye movements, the cerebellum acts as a precise calibrator, ensuring smooth pursuit and gaze stability. Cerebellar lesions disrupt this delicate balance, leading to various types of nystagmus.
In my practice, I’ve observed that cerebellar damage often results in:
- Impaired gaze-holding ability
- Disrupted vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR)
- Decreased ability to suppress unwanted eye movements
These factors combine to produce the characteristic nystagmus we associate with cerebellar lesions.
Types of Nystagmus Associated with Cerebellar Damage
Cerebellar lesions can manifest in several distinct forms of nystagmus. As a specialist, I’ve encountered and studied these variants extensively:
- Downbeat Nystagmus: Often seen in lesions affecting the vestibulocerebellum, particularly the flocculus and paraflocculus.
- Gaze-Evoked Nystagmus: Common in diffuse cerebellar disorders, this type of nystagmus is exacerbated when looking to the sides.
- Rebound Nystagmus: A unique form where the eyes drift slowly in one direction, followed by a quick correction in the opposite direction after returning to the primary position.
- Periodic Alternating Nystagmus: An intriguing variant where the direction of nystagmus changes every few minutes, often associated with lesions in the cerebellar nodulus.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment.
Diagnosing Cerebellar Lesions Through Nystagmus Patterns
As a neuro-ophthalmologist, I can’t stress enough the importance of careful observation and specialized testing in diagnosing cerebellar lesions through nystagmus patterns.
Key diagnostic approaches include:
- Detailed Ocular Motility Examination: This involves observing eye movements in various gaze positions and during different tasks.
- Video-oculography: This advanced technique allows for precise measurement and analysis of eye movements, revealing subtle patterns that might be missed by the naked eye.
- Vestibular Function Tests: These help differentiate between peripheral and central causes of nystagmus.
- Neuroimaging: MRI scans are invaluable in pinpointing the exact location and extent of cerebellar lesions.
- Ophthalmological Assessment: A comprehensive eye exam helps rule out other potential causes of nystagmus.
By combining these approaches, we can not only confirm the presence of cerebellar lesions but also gain insights into their specific location and severity.
Treatment Approaches for Nystagmus Caused by Cerebellar Lesions
Managing nystagmus resulting from cerebellar lesions requires a multifaceted approach. In my years of practice, I’ve found that a combination of the following strategies often yields the best results:
- Pharmacological Interventions: Medications such as gabapentin, baclofen, or memantine can help reduce nystagmus in some patients.
- Optical Devices: Prism glasses or contact lenses can sometimes alleviate symptoms by shifting the null point of nystagmus.
- Vestibular Rehabilitation: Specialized exercises can improve gaze stability and reduce the impact of nystagmus on daily activities.
- Surgical Options: In severe cases, procedures like tenotomy or artificial divergence may be considered to dampen nystagmus.
- Treating Underlying Causes: When possible, addressing the root cause of cerebellar damage (e.g., removing tumors or managing inflammatory conditions) is crucial.
- Adaptive Technologies: For patients with persistent symptoms, visual aids and assistive devices can significantly improve quality of life.
It’s important to note that treatment plans should be tailored to each individual, taking into account the specific type of nystagmus, its severity, and the patient’s overall health status.
Expanding Your Knowledge: Essential Resources for Understanding Nystagmus
As a neuro-ophthalmologist, I often emphasize the importance of patient education. While this article provides a solid foundation, those seeking a deeper understanding of nystagmus, especially in the context of cerebellar lesions, may benefit from additional resources.
In my practice, I’ve found that well-informed patients are better equipped to manage their condition and engage productively with their healthcare team. To this end, I recommend exploring comprehensive guides that delve into the intricacies of nystagmus.
One such resource that has gained recognition in the field is a recently published comprehensive guide on nystagmus. This type of resource typically offers:
- Cutting-edge research insights: Stay abreast of the latest discoveries in nystagmus pathophysiology and treatment.
- Lifecycle management strategies: Understand how to adapt care approaches as patients age or their condition evolves.
- Practical coping mechanisms: Learn techniques to minimize the impact of nystagmus on daily activities.
- Treatment deep-dives: Gain a thorough understanding of both established and emerging treatment modalities.
- Patient narratives: Draw inspiration and insights from real-life experiences of individuals living with nystagmus.
By delving into such comprehensive resources, patients and their families can:
- Develop a more nuanced understanding of their condition
- Engage in more informed discussions with their healthcare providers
- Make well-reasoned decisions about their treatment plans
- Feel more empowered in managing their health
As we continue to make strides in understanding and treating nystagmus, staying informed becomes increasingly crucial. By arming yourself with knowledge, you become an active participant in your healthcare journey, potentially leading to better outcomes and improved quality of life.
Remember, if you’re experiencing symptoms of nystagmus or have concerns about cerebellar function, don’t hesitate to consult with a neuro-ophthalmologist. Early diagnosis and intervention can make a significant difference in managing these conditions effectively.